Building a Measurable RAG System with Quarkus Easy RAG, LangChain4j, and Ollama
How Java developers can build, evaluate, and trust Retrieval-Augmented Generation using Quarkus, LangChain4j, and local LLMs
Retrieval-Augmented Generation works until it quietly stops working.
Answers still sound confident. Latency looks fine. Nothing crashes.
And yet, the system slowly drifts into hallucinations, partial answers, or irrelevant context.
This tutorial is about preventing that failure mode.
We will build a complete, local RAG system using Quarkus, LangChain4j, and Ollama, and then instrument it with evaluation metrics so you can measure whether your RAG pipeline is still behaving correctly.
Not a simple RAG demo. A system you can reason about.
Why RAG Fails Quietly in Production
Most developers think RAG is about retrieval quality.
Get better embeddings. Tune chunk size. Increase topK. Done.
That mental model fails in real systems.
What actually breaks in production is alignment between retrieval, generation, and grounding. The retriever returns relevant text, but the model ignores half of it. Or it combines multiple documents into a fluent but incorrect answer. Or it answers the wrong question convincingly.
Without evaluation, you only find this out when users complain.
This tutorial assumes a different stance:
RAG is a pipeline, not a feature
Every pipeline needs observability
LLM output must be scored, not trusted
We will build evaluation into the request path itself.
What We’ll Build
RAG System using Quarkus Easy RAG (auto-ingestion of documents)
Evaluation Pipeline with RAGAS, BLEU, and Semantic Similarity metrics
Complete Working Example with a product documentation chatbot
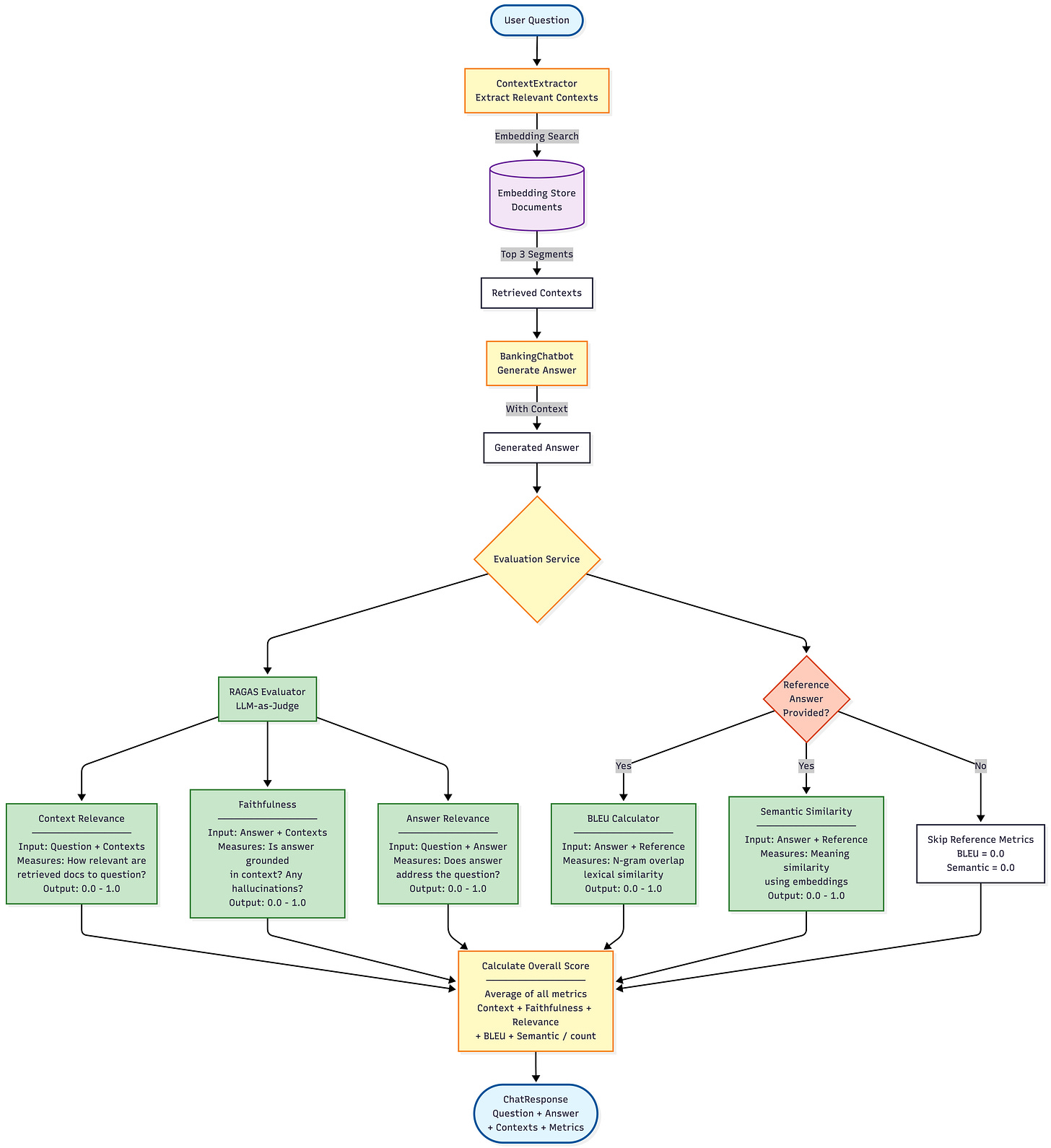
Here is an overview of the application flow at a glance:
Prerequisites
Java 17 or higher
Maven 3.8+
Docker (for Ollama)
10GB disk space for models
We deliberately run everything locally. If you cannot reason about RAG locally, you cannot reason about it in Kubernetes.
Create Quarkus Project with Easy RAG
mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:create \
-DprojectGroupId=com.example \
-DprojectArtifactId=rag-chatbot-eval \
-Dextensions="quarkus-langchain4j-easy-rag,quarkus-langchain4j-ollama,rest-jackson" \
-DclassName="com.example.ChatbotResource" \
-Dpath="/chat"
cd rag-chatbot-evalAdd Additional Dependencies
Add to your pom.xml:
<!-- For metrics calculation -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-text</artifactId>
<version>1.15.0</version>
</dependency>Create Sample Documents
Create a directory structure:
mkdir -p src/main/resources/documentsCreate src/main/resources/documents/banking-products.txt:
Standard Savings Account
Our Standard Savings Account offers competitive interest rates with no monthly fees.
Key features include:
- 2.5% annual interest rate
- No minimum balance requirement
- Free online and mobile banking
- FDIC insured up to $250,000
- Easy access to your funds
- Monthly account statements
This account is perfect for customers who want to start saving with flexibility
and no commitments.Create src/main/resources/documents/premium-account.txt:
Premium Checking Account
The Premium Checking Account is designed for customers who value premium services.
Features include:
- No ATM fees worldwide
- Free checks and money orders
- Dedicated customer service line
- Travel insurance coverage
- Purchase protection
- 0.5% cashback on debit card purchases
- Monthly fee: $15 (waived with $5,000 minimum balance)
Ideal for frequent travelers and customers who want enhanced banking benefits.Create src/main/resources/documents/loan-products.txt:
Personal Loan Options
We offer flexible personal loans for various needs:
Home Improvement Loans:
- Rates starting at 5.99% APR
- Loan amounts: $5,000 to $100,000
- Terms: 1 to 7 years
- No prepayment penalties
Auto Loans:
- Rates as low as 3.99% APR for new cars
- Up to 100% financing available
- Terms up to 72 months
- Pre-approval in minutes
All loans subject to credit approval. Visit a branch or apply online for more information.Step 5: Configure Application
Create/update src/main/resources/application.properties:
# Easy RAG Configuration
quarkus.langchain4j.easy-rag.path=src/main/resources/documents
quarkus.langchain4j.easy-rag.path-matcher=glob:**.txt
quarkus.langchain4j.easy-rag.max-segment-size=400
quarkus.langchain4j.easy-rag.max-overlap-size=50
quarkus.langchain4j.easy-rag.max-results=3
quarkus.langchain4j.easy-rag.recursive=true
# Reuse embeddings for faster dev mode restarts
quarkus.langchain4j.easy-rag.reuse-embeddings.enabled=true
quarkus.langchain4j.easy-rag.reuse-embeddings.file=banking-embeddings.json
# Ollama Chat Model Configuration
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.timeout=60s
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.chat-model.model-id=llama3.2
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.chat-model.temperature=0.5
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.chat-model.timeout=60s
# Ollama Embedding Model Configuration
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.embedding-model.model-id=nomic-embed-textPart 2: Create the RAG-Powered Chatbot
Create AI Service Interface
package com.example.service;
import dev.langchain4j.service.SystemMessage;
import dev.langchain4j.service.UserMessage;
import io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.RegisterAiService;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
@ApplicationScoped
@RegisterAiService // no need to declare a retrieval augmentor here, it is automatically generated
// and discovered
public interface BankingChatbot {
@SystemMessage("""
You are a helpful banking assistant. Answer questions about our banking products
using the information provided in the context. If you don't know the answer,
say so politely. Be concise but informative.
""")
String chat(@UserMessage String userMessage);
}Create Domain Models
Create the following files:
// src/main/java/com/example/model/ChatRequest.java
package com.example.model;
public class ChatRequest {
public String question;
public String referenceAnswer; // Optional, for evaluation
public ChatRequest() {
}
public ChatRequest(String question) {
this.question = question;
}
}
// src/main/java/com/example/model/ChatResponse.java
package com.example.model;
import java.util.List;
public class ChatResponse {
public String question;
public String answer;
public List<String> retrievedContexts;
public EvaluationMetrics metrics;
public ChatResponse() {}
}
// src/main/java/com/example/model/EvaluationMetrics.java
package com.example.model;
public class EvaluationMetrics {
public double contextRelevance;
public double faithfulness;
public double answerRelevance;
public double bleuScore;
public double semanticSimilarity;
public double overallScore;
public EvaluationMetrics() {}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format(
"Metrics[context=%.2f, faithfulness=%.2f, relevance=%.2f, bleu=%.2f, semantic=%.2f, overall=%.2f]",
contextRelevance, faithfulness, answerRelevance, bleuScore, semanticSimilarity, overallScore
);
}
}Implement Evaluation Metrics
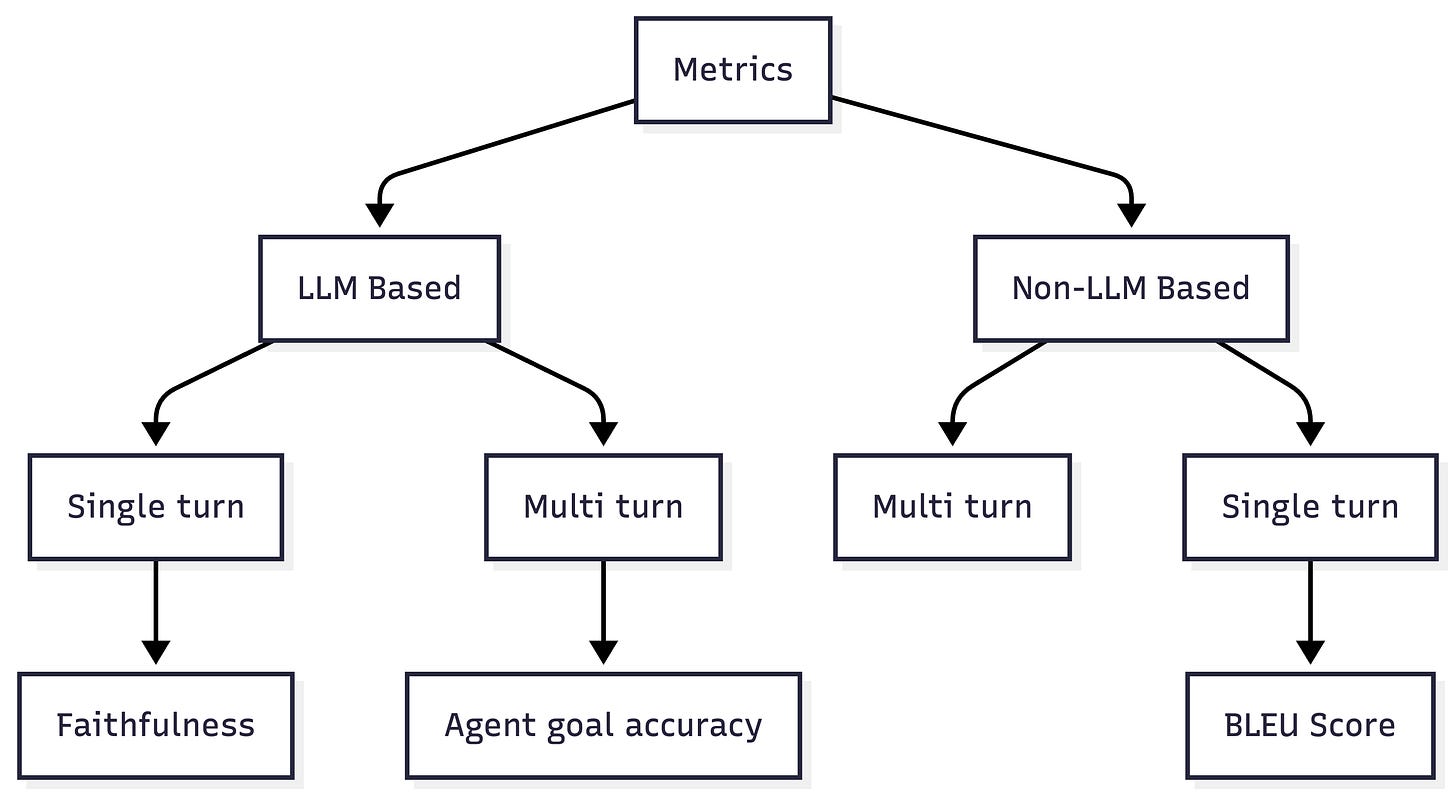
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Metrics are the feedback loop that makes iteration possible. Especially in AI infused systems, you need to ensure to run a lot of evaluations to continuously monitor applications. RAGAS groups metrics according to the following outline:
For this tutorial, we are just taking a few examples from the complete list so you get an idea for the metrics categories and implementations. You can and should learn more and read more about RAGAS and metrics.
BLEU Score Calculator
The BleuScore metric is used to evaluate the quality of response by comparing it with reference. It measures the similarity between the response and the reference based on n-gram precision and brevity penalty. BLEU score was originally designed to evaluate machine translation systems, but it is also used in other natural language processing tasks. BLEU score ranges from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates a perfect match between the response and the reference. We use a simplified version below.
Create: src/main/java/com/example/metrics/BleuCalculator.java
package com.example.metrics;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
@ApplicationScoped
public class BleuCalculator {
/**
* Calculate BLEU score with n-gram precision up to 4-grams
*/
public double calculateBleu(String candidate, String reference) {
if (candidate == null || reference == null ||
candidate.trim().isEmpty() || reference.trim().isEmpty()) {
return 0.0;
}
List<String> candidateTokens = tokenize(candidate);
List<String> referenceTokens = tokenize(reference);
if (candidateTokens.isEmpty() || referenceTokens.isEmpty()) {
return 0.0;
}
// Calculate precision for 1-gram to 4-gram
double[] precisions = new double[4];
double[] weights = { 0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25 };
for (int n = 1; n <= 4; n++) {
precisions[n - 1] = calculateNGramPrecision(candidateTokens, referenceTokens, n);
}
// Geometric mean of precisions
double logSum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (precisions[i] > 0) {
logSum += weights[i] * Math.log(precisions[i]);
} else {
return 0.0; // If any precision is 0, BLEU is 0
}
}
double geometricMean = Math.exp(logSum);
// Brevity penalty
double brevityPenalty = calculateBrevityPenalty(
candidateTokens.size(),
referenceTokens.size());
return brevityPenalty * geometricMean;
}
private double calculateNGramPrecision(List<String> candidate,
List<String> reference,
int n) {
Map<String, Integer> candidateNGrams = getNGrams(candidate, n);
Map<String, Integer> referenceNGrams = getNGrams(reference, n);
int matchCount = 0;
int totalCount = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : candidateNGrams.entrySet()) {
String ngram = entry.getKey();
int candidateCount = entry.getValue();
int referenceCount = referenceNGrams.getOrDefault(ngram, 0);
matchCount += Math.min(candidateCount, referenceCount);
totalCount += candidateCount;
}
return totalCount > 0 ? (double) matchCount / totalCount : 0.0;
}
private Map<String, Integer> getNGrams(List<String> tokens, int n) {
Map<String, Integer> ngrams = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= tokens.size() - n; i++) {
String ngram = String.join(" ", tokens.subList(i, i + n));
ngrams.put(ngram, ngrams.getOrDefault(ngram, 0) + 1);
}
return ngrams;
}
private double calculateBrevityPenalty(int candidateLength, int referenceLength) {
if (candidateLength > referenceLength) {
return 1.0;
}
return Math.exp(1.0 - (double) referenceLength / candidateLength);
}
private List<String> tokenize(String text) {
return Arrays.stream(text.toLowerCase()
.replaceAll("[^a-z0-9\\s]", "")
.split("\\s+"))
.filter(s -> !s.isEmpty())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}RAGAS Evaluator
Ragas provides a set of evaluation metrics that can be used to measure the performance of your LLM application. These metrics are designed to help you objectively measure the performance of your application. Metrics are available for different applications and tasks, such as RAG and Agentic workflows. For this demo, we are just using a subset of them. So this is a very lightweight version.
with only scores:
Context relevance
Faithfulness
Answer relevance
Create: src/main/java/com/example/metrics/RagasEvaluator.java
package com.example.metrics;
import java.util.List;
import dev.langchain4j.model.chat.ChatModel;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
@ApplicationScoped
public class RagasEvaluator {
@Inject
ChatModel chatModel;
/**
* Context Relevance: How relevant are the retrieved documents to the question?
*/
public double evaluateContextRelevance(String question, List<String> contexts) {
if (contexts == null || contexts.isEmpty()) {
return 0.0;
}
StringBuilder contextText = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < contexts.size(); i++) {
contextText.append("Context ").append(i + 1).append(": ")
.append(contexts.get(i)).append("\n\n");
}
String prompt = String.format("""
Question: %s
Retrieved Contexts:
%s
Task: Rate how relevant the provided contexts are to answering the question.
Consider if the contexts contain information needed to answer the question.
Respond with ONLY a number between 0.0 and 1.0, where:
- 0.0 = completely irrelevant
- 1.0 = perfectly relevant
Score:""", question, contextText.toString());
return parseScore(chatModel.chat(prompt));
}
/**
* Faithfulness: Is the answer grounded in the provided context?
*/
public double evaluateFaithfulness(String answer, List<String> contexts) {
if (answer == null || answer.trim().isEmpty() || contexts == null || contexts.isEmpty()) {
return 0.0;
}
StringBuilder contextText = new StringBuilder();
for (String context : contexts) {
contextText.append(context).append("\n\n");
}
String prompt = String.format("""
Retrieved Context:
%s
Generated Answer: %s
Task: Evaluate if the answer is faithful to the context.
Check if all claims in the answer can be verified from the context.
An answer is faithful if it doesn't add information not present in the context.
Respond with ONLY a number between 0.0 and 1.0, where:
- 0.0 = completely unfaithful (hallucinated content)
- 1.0 = perfectly faithful (all claims supported by context)
Score:""", contextText.toString(), answer);
return parseScore(chatModel.chat(prompt));
}
/**
* Answer Relevance: Does the answer actually address the question?
*/
public double evaluateAnswerRelevance(String question, String answer) {
if (question == null || answer == null ||
question.trim().isEmpty() || answer.trim().isEmpty()) {
return 0.0;
}
String prompt = String.format("""
Question: %s
Generated Answer: %s
Task: Rate how well the answer addresses the question.
Consider if the answer is on-topic and provides useful information.
Respond with ONLY a number between 0.0 and 1.0, where:
- 0.0 = completely irrelevant to the question
- 1.0 = perfectly relevant and complete answer
Score:""", question, answer);
return parseScore(chatModel.chat(prompt));
}
private double parseScore(String response) {
try {
// Extract number from response
String cleaned = response.trim()
.replaceAll("[^0-9.]", "")
.trim();
if (cleaned.isEmpty()) {
System.err.println("No numeric value found in response: " + response);
return 0.5;
}
double score = Double.parseDouble(cleaned);
return Math.max(0.0, Math.min(1.0, score)); // Clamp between 0 and 1
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.err.println("Failed to parse score from: " + response);
return 0.5; // Default middle score if parsing fails
}
}
}Semantic Similarity Calculator
The Semantic Similarity metric evaluates the semantic resemblance between a generated response and a reference (ground truth) answer. It ranges from 0 to 1, with higher scores indicating better alignment between the generated answer and the ground truth.
Create: src/main/java/com/example/metrics/SemanticSimilarityCalculator.java
package com.example.metrics;
import dev.langchain4j.data.embedding.Embedding;
import dev.langchain4j.model.embedding.EmbeddingModel;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
@ApplicationScoped
public class SemanticSimilarityCalculator {
@Inject
EmbeddingModel embeddingModel;
/**
* Calculate cosine similarity between two texts using embeddings
*/
public double calculateSimilarity(String text1, String text2) {
if (text1 == null || text2 == null ||
text1.trim().isEmpty() || text2.trim().isEmpty()) {
return 0.0;
}
try {
Embedding embedding1 = embeddingModel.embed(text1).content();
Embedding embedding2 = embeddingModel.embed(text2).content();
return cosineSimilarity(embedding1.vector(), embedding2.vector());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error calculating semantic similarity: " + e.getMessage());
return 0.0;
}
}
private double cosineSimilarity(float[] vectorA, float[] vectorB) {
if (vectorA.length != vectorB.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vectors must have same dimensions");
}
double dotProduct = 0.0;
double normA = 0.0;
double normB = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < vectorA.length; i++) {
dotProduct += vectorA[i] * vectorB[i];
normA += Math.pow(vectorA[i], 2);
normB += Math.pow(vectorB[i], 2);
}
if (normA == 0.0 || normB == 0.0) {
return 0.0;
}
return dotProduct / (Math.sqrt(normA) * Math.sqrt(normB));
}
}Create Evaluation Service with Context Extraction
Context Extraction Utility
Create: src/main/java/com/example/service/ContextExtractor.java
package com.example.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import dev.langchain4j.data.embedding.Embedding;
import dev.langchain4j.data.segment.TextSegment;
import dev.langchain4j.model.embedding.EmbeddingModel;
import dev.langchain4j.store.embedding.EmbeddingMatch;
import dev.langchain4j.store.embedding.EmbeddingSearchRequest;
import dev.langchain4j.store.embedding.EmbeddingSearchResult;
import dev.langchain4j.store.embedding.EmbeddingStore;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
@ApplicationScoped
public class ContextExtractor {
@Inject
EmbeddingStore<TextSegment> embeddingStore;
@Inject
EmbeddingModel embeddingModel;
/**
* Extract relevant contexts for a given question
*/
public List<String> extractContexts(String question, int maxResults) {
// Generate embedding for the question
Embedding questionEmbedding = embeddingModel.embed(question).content();
// Search for relevant segments
EmbeddingSearchRequest searchRequest = EmbeddingSearchRequest.builder()
.queryEmbedding(questionEmbedding)
.maxResults(maxResults)
.minScore(0.5) // Optional: filter by relevance score
.build();
EmbeddingSearchResult<TextSegment> searchResult = embeddingStore.search(searchRequest);
// Extract text from matched segments
return searchResult.matches().stream()
.map(EmbeddingMatch::embedded)
.map(TextSegment::text)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}Complete Evaluation Service
Create: src/main/java/com/example/service/RagEvaluationService.java
package com.example.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.jboss.logging.Logger;
import com.example.metrics.BleuCalculator;
import com.example.metrics.RagasEvaluator;
import com.example.metrics.SemanticSimilarityCalculator;
import com.example.model.ChatRequest;
import com.example.model.ChatResponse;
import com.example.model.EvaluationMetrics;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
@ApplicationScoped
public class RagEvaluationService {
private static final Logger LOG = Logger.getLogger(RagEvaluationService.class);
@Inject
BankingChatbot chatbot;
@Inject
ContextExtractor contextExtractor;
@Inject
RagasEvaluator ragasEvaluator;
@Inject
BleuCalculator bleuCalculator;
@Inject
SemanticSimilarityCalculator semanticCalculator;
/**
* Process a chat request and evaluate the response
*/
public ChatResponse processAndEvaluate(ChatRequest request) {
LOG.infof("Processing question: %s", request.question);
// Step 1: Extract relevant contexts
List<String> contexts = contextExtractor.extractContexts(request.question, 3);
LOG.infof("Retrieved %d context segments", contexts.size());
// Step 2: Generate answer using RAG
String answer = chatbot.chat(request.question);
LOG.infof("Generated answer: %s", answer);
// Step 3: Evaluate the response
EvaluationMetrics metrics = evaluateResponse(
request.question,
answer,
contexts,
request.referenceAnswer);
// Step 4: Build response
ChatResponse response = new ChatResponse();
response.question = request.question;
response.answer = answer;
response.retrievedContexts = contexts;
response.metrics = metrics;
LOG.infof("Evaluation complete: %s", metrics);
return response;
}
/**
* Evaluate a RAG response using multiple metrics
*/
private EvaluationMetrics evaluateResponse(String question,
String answer,
List<String> contexts,
String referenceAnswer) {
EvaluationMetrics metrics = new EvaluationMetrics();
// RAGAS Metrics (always computed)
try {
metrics.contextRelevance = ragasEvaluator.evaluateContextRelevance(question, contexts);
metrics.faithfulness = ragasEvaluator.evaluateFaithfulness(answer, contexts);
metrics.answerRelevance = ragasEvaluator.evaluateAnswerRelevance(question, answer);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.errorf("Error computing RAGAS metrics: %s", e.getMessage());
}
// Reference-based metrics (only if reference answer provided)
if (referenceAnswer != null && !referenceAnswer.trim().isEmpty()) {
try {
metrics.bleuScore = bleuCalculator.calculateBleu(answer, referenceAnswer);
metrics.semanticSimilarity = semanticCalculator.calculateSimilarity(answer, referenceAnswer);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.errorf("Error computing reference-based metrics: %s", e.getMessage());
}
}
// Calculate overall score
metrics.overallScore = calculateOverallScore(metrics);
return metrics;
}
private double calculateOverallScore(EvaluationMetrics metrics) {
double sum = metrics.contextRelevance + metrics.faithfulness + metrics.answerRelevance;
int count = 3;
if (metrics.bleuScore > 0) {
sum += metrics.bleuScore;
count++;
}
if (metrics.semanticSimilarity > 0) {
sum += metrics.semanticSimilarity;
count++;
}
return count > 0 ? sum / count : 0.0;
}
}The REST API
Create: src/main/java/com/example/ChatbotResource.java
package com.example;
import org.jboss.logging.Logger;
import com.example.model.ChatRequest;
import com.example.model.ChatResponse;
import com.example.service.RagEvaluationService;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
import jakarta.ws.rs.Consumes;
import jakarta.ws.rs.GET;
import jakarta.ws.rs.POST;
import jakarta.ws.rs.Path;
import jakarta.ws.rs.Produces;
import jakarta.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
@Path("/chat")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public class ChatbotResource {
private static final Logger LOG = Logger.getLogger(ChatbotResource.class);
@Inject
RagEvaluationService evaluationService;
@POST
public ChatResponse chat(ChatRequest request) {
LOG.infof("Received chat request: %s", request.question);
return evaluationService.processAndEvaluate(request);
}
@GET
@Path("/health")
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
public String health() {
return "Banking Chatbot with Evaluation is running!";
}
}Testing the Complete System
Start the Application
# Start Quarkus in dev mode
mvn quarkus:devTest with Simple Question
Create test-simple.json:
{
"question": "What are the benefits of a standard savings account?"
}Test:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @test-simple.json | jqExpected response:
{
"question": "What are the benefits of a standard savings account?",
"answer": "Our Standard Savings Account offers several benefits, including:\n\n* Competitive interest rate of 2.5% annual interest rate\n* No monthly fees\n* Free online and mobile banking\n* FDIC insurance up to $250,000\n* Easy access to your funds\n* Monthly account statements\n\nThis account is perfect for customers who want to start saving with flexibility and no commitments.",
"retrievedContexts": [
"[...]"
],
"metrics": {
"contextRelevance": 0.5,
"faithfulness": 0.7,
"answerRelevance": 0.5,
"bleuScore": 0.0,
"semanticSimilarity": 0.0,
"overallScore": 0.5666666666666667
}
}Test with Reference Answer (Full Evaluation)
Create test-with-reference.json:
{
"question": "What is the interest rate for the standard savings account?",
"referenceAnswer": "The standard savings account offers a 2.5% annual interest rate."
}Test:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @test-with-reference.json | jqExpected response with all metrics:
{
"question": "What is the interest rate for the standard savings account?",
"answer": "The interest rate for our Standard Savings Account is 2.5% annual interest rate, with no minimum balance requirement and no monthly fees.",
"retrievedContexts": [
"[...]"
],
"metrics": {
"contextRelevance": 0.5,
"faithfulness": 0.8,
"answerRelevance": 0.8,
"bleuScore": 0.161692143534558,
"semanticSimilarity": 0.7843242341979497,
"overallScore": 0.6092032755465016
}
}Test with Multiple Questions
Create test-batch.sh:
#!/bin/bash
questions=(
"What are the fees for the premium checking account?"
"What types of personal loans do you offer?"
"What is the APR for auto loans?"
"Can I get travel insurance with my account?"
)
for q in "${questions[@]}"; do
echo "Testing: $q"
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{\"question\": \"$q\"}" | jq '.metrics'
echo "---"
sleep 2
doneRun:
chmod +x test-batch.sh
./test-batch.shUnderstanding the Metrics
High relevance + low faithfulness means the model ignored the context.
High faithfulness + low relevance means retrieval failed.
Low everything means your documents are wrong.
Interpreting Scores
Context Relevance (0.0 - 1.0)
0.9-1.0: Excellent - Retrieved docs perfectly match the question
0.7-0.89: Good - Most relevant information is present
0.5-0.69: Fair - Some relevant information, but gaps exist
<0.5: Poor - Retrieved docs don’t match the question
Faithfulness (0.0 - 1.0)
0.9-1.0: Excellent - Answer fully grounded in context, no hallucinations
0.7-0.89: Good - Mostly accurate with minor additions
0.5-0.69: Fair - Some hallucinated content
<0.5: Poor - Significant hallucinations
Answer Relevance (0.0 - 1.0)
0.9-1.0: Excellent - Directly answers the question
0.7-0.89: Good - Addresses the question with minor tangents
0.5-0.69: Fair - Partially relevant
<0.5: Poor - Answer doesn’t address the question
BLEU Score (0.0 - 1.0) - Only with reference answer
0.7-1.0: High lexical overlap with reference
0.4-0.69: Moderate overlap, similar wording
0.2-0.39: Low overlap, different wording
<0.2: Very different from reference
Semantic Similarity (0.0 - 1.0) - Only with reference answer
0.85-1.0: Nearly identical meaning
0.7-0.84: Similar meaning, different expression
0.5-0.69: Related but divergent
<0.5: Different meanings
Next Steps to level this demo up
Add More Documents: Expand your knowledge base
Implement Reranking: Improve retrieval quality with rerankers
Create Web UI: Build a React/Angular frontend
Add Contextual RAG: Use Claude’s contextual embeddings
Deploy to Production: Use Kubernetes with persistent stores
A/B Testing: Compare different RAG configurations
Multi-Language Support: Test with documents in various languages
We built a RAG system that can explain itself when it fails.
Easy RAG makes document ingestion effortless - just point to a directory
Ollama enables completely local, cost-free RAG systems
RAGAS provides comprehensive, LLM-based evaluation without references
BLEU + Semantic Similarity add reference-based validation
Quarkus Integration gives you production-ready features out-of-the-box
Combined Metrics provide holistic view of RAG system quality
If you cannot measure it, you do not own it.